If you suspect you might be pregnant, taking a pregnancy test is the first step in confirming your pregnancy. A pregnancy test works by detecting the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced by the placenta after fertilization.
While the accuracy of a pregnancy test depends on many factors, one important consideration is the freshness of the urine used in the test. But how long can you keep your urine for a pregnancy test, and what happens if you wait too long to test it?
In this blog post, we will explore the guidelines for storing urine for pregnancy testing, how long urine can be stored for accurate results, and what factors can affect urine quality. We will also provide tips and best practices for taking a pregnancy test to ensure the most accurate results.
How Long Can You Keep Your Urine For A Pregnancy Test?
The recommended time frame for using urine for a pregnancy test is usually specified in the instructions provided with the test. Generally, it is recommended to use urine that is collected on the day of the test or shortly before to ensure the most accurate results.
However, some tests may allow for urine that has been stored for a few days, provided it has been stored properly in a clean, dry container in a cool place. The exact length of time that urine can be stored for a pregnancy test may vary depending on the specific test and the storage conditions, so it is important to follow the instructions provided with the test carefully.
It is important to note that waiting too long to test the urine can lead to a false negative result, even if the woman is actually pregnant. This is because the concentration of hCG in the urine may decrease over time, making it harder to detect with the test. Additionally, if the urine is not stored properly or if it is contaminated, it can also lead to inaccurate results.
Therefore, it is essential to follow the guidelines for storing urine for pregnancy testing and to use urine within the recommended time frame for the most accurate results. If there are any concerns or questions about the accuracy of a pregnancy test result, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider.
Understanding Pregnancy Tests
Types Of Pregnancy Tests
There are several types of pregnancy tests available for women who suspect they may be pregnant. These tests vary in their method of detection, sensitivity, and convenience. Here are the most common types of pregnancy tests:
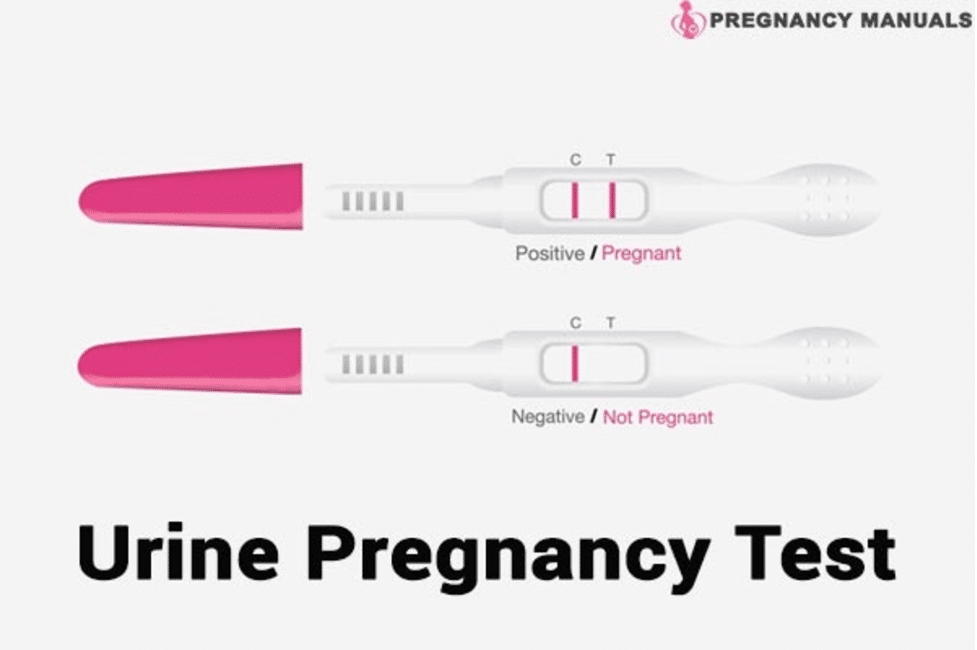
- Urine Tests: These are the most commonly used pregnancy tests, and they work by detecting the presence of hCG in the urine. Urine tests can be done at home using a test kit that can be purchased over the counter or through a healthcare provider. The test kit includes a test strip or a test stick that is dipped in a urine sample or held in the urine stream. Results are usually available within a few minutes, with one line indicating a negative result and two lines indicating a positive result.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are more sensitive than urine tests and can detect pregnancy earlier, sometimes even before a missed period. There are two types of blood tests for pregnancy: quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative blood tests measure the exact amount of hCG in the blood, while qualitative blood tests simply confirm the presence of hCG. Blood tests are usually done in a healthcare provider’s office and can take a few hours to a few days to get the results.
- Digital Tests: Digital tests work like urine tests, but instead of displaying lines, they display a message that reads “pregnant” or “not pregnant” on a digital screen. Digital tests are easy to use and may be more accurate than traditional urine tests.
- Saliva Tests: Saliva tests detect the presence of hCG in the saliva, and are easy to use and non-invasive. However, saliva tests are not as reliable as urine or blood tests and may not be widely available.
- Homemade Tests: Homemade pregnancy tests involve using household items such as vinegar, sugar, toothpaste, or bleach to detect the presence of hCG in the urine. These tests are not reliable and are not recommended for accurate pregnancy detection.
It is important to follow the instructions provided with the pregnancy test carefully and to consult with a healthcare provider if there are any questions or concerns about the accuracy of the results.
How Pregnancy Tests Work?
Pregnancy tests work by detecting the presence of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a woman’s urine or blood. This hormone is produced by the developing placenta after the fertilized egg implants in the uterus, and its levels increase rapidly in the first few weeks of pregnancy.
Here is how the most common types of pregnancy tests work:
- Urine Tests: Urine tests detect the presence of hCG in the urine. A woman collects a urine sample and either dips a test strip into the urine or holds a test stick in the urine stream. The test strip or stick contains chemicals that react with hCG, producing a visible line or other indication of a positive result.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests also detect the presence of hCG in the blood. There are two types of blood tests for pregnancy: quantitative and qualitative. A quantitative blood test measures the exact amount of hCG in the blood, while a qualitative blood test simply confirms the presence of hCG.
- Digital Tests: Digital tests work like urine tests, but instead of displaying lines, they display a message that reads “pregnant” or “not pregnant” on a digital screen. Digital tests are more accurate than traditional urine tests and may be easier to read.
Pregnancy tests are designed to be highly sensitive to hCG, but there are some factors that can affect their accuracy. For example, taking the test too early may result in a false negative result, as hCG levels may not be high enough to detect. In addition, certain medications or medical conditions can affect hCG levels and lead to inaccurate results.
It is important to follow the instructions provided with the pregnancy test carefully and to consult with a healthcare provider if there are any questions or concerns about the accuracy of the results. A healthcare provider can also perform a more sensitive blood test to confirm a pregnancy or rule out any other medical conditions that may be causing symptoms.
When To Take A Pregnancy Test?
If you suspect you may be pregnant, the timing of when to take a pregnancy test is important for accurate results. Here are some general guidelines to help determine when to take a pregnancy test:
- Wait for a missed period: Most pregnancy tests are designed to detect hCG levels in the urine or blood after a missed period. Waiting until after a missed period increases the accuracy of the test results. However, some tests are sensitive enough to detect pregnancy even before a missed period.
- Check the instructions: Every pregnancy test has specific instructions for use, including the recommended time to take the test. It is important to carefully read and follow the instructions for the specific test you are using.
- Consider the sensitivity of the test: Some pregnancy tests are more sensitive than others and can detect pregnancy earlier. These tests may be more expensive, but can provide earlier results. If you are unsure about the sensitivity of the test you are using, consult with a healthcare provider.
- Know your menstrual cycle: If you have irregular periods, it may be more difficult to determine when to take a pregnancy test. In this case, a healthcare provider may recommend waiting a certain amount of time after a missed period, or conducting multiple tests over several days to increase the accuracy of the results.
- Consider other symptoms: If you are experiencing other symptoms of pregnancy, such as nausea, breast tenderness, or fatigue, it may be a good idea to take a pregnancy test to confirm or rule out pregnancy.
Ultimately, the timing of when to take a pregnancy test may vary depending on individual circumstances. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns about taking a pregnancy test or if you experience any unusual symptoms.
Urine Collection And Storage
How To Collect Urine For A Pregnancy Test?
Collecting urine for a pregnancy test is a simple process, but it is important to follow the instructions carefully to ensure accurate results. Here are the steps to follow:
- Choose the right time: The best time to collect urine for a pregnancy test is usually in the morning, as hCG levels are more concentrated in the first morning urine. However, if you need to take the test at another time, make sure to hold your urine for at least a few hours before collecting a sample.
- Gather supplies: Most pregnancy tests come with a test stick or strip and a collection cup. If your test does not come with a cup, use a clean and dry cup or container to collect the urine.
- Clean the area: Wash your hands and genital area with soap and water to ensure cleanliness and reduce the risk of contamination.
- Collect the urine: Hold the collection cup or container under your urine stream and collect a sample of midstream urine. This means starting to urinate briefly into the toilet, then holding the cup under your stream to collect the middle portion of your urine.
- Use the urine for the test: Once you have collected the urine, follow the instructions provided with the pregnancy test to dip the test strip or stick into the urine, or to hold the stick in the urine stream.
- Dispose of the urine: After using the urine for the test, dispose of it in a safe and appropriate manner. Do not reuse the cup or container for any other purpose.
It is important to follow the instructions provided with your specific pregnancy test to ensure accurate results. If you have any questions or concerns about collecting urine for a pregnancy test, consult with a healthcare provider.
Importance Of Storing Urine Properly
Proper storage of urine is essential when it comes to conducting a pregnancy test or any other medical test. The way urine is stored can impact the accuracy and reliability of the test results. Here are some reasons why proper storage of urine is important:
- Prevents contamination: Urine is a bodily fluid that can easily become contaminated with bacteria, viruses, or other substances that can affect the test results. Proper storage in a clean and sterile container can help prevent contamination and ensure accurate results.
- Maintains integrity of the sample: Improper storage of urine can result in the breakdown of the sample, leading to inaccurate test results. Urine that is exposed to light, heat, or air for extended periods of time can lead to changes in the composition of the sample, affecting the accuracy of the test.
- Allows for repeated testing: Properly stored urine can be used for repeat testing if necessary. In some cases, a healthcare provider may need to retest a urine sample to confirm or rule out a diagnosis. Proper storage can ensure that the sample is available for repeat testing if needed.
- Facilitates transport: If a urine sample needs to be transported to a laboratory for testing, proper storage can help ensure the sample arrives at the laboratory in the same condition as when it was collected. This can help maintain the integrity of the sample and prevent errors in the testing process.
Overall, proper storage of urine is essential to ensure accurate and reliable test results. Following the instructions provided with the pregnancy test or any other medical test can help ensure that the urine is collected and stored properly. If you have any questions or concerns about storing urine for a test, consult with a healthcare provider.
Factors That Can Affect Urine Quality
Urine is an important bodily fluid that can provide valuable insights into a person’s health. However, there are several factors that can affect the quality of urine and potentially impact the accuracy of any medical tests conducted with it. Here are some factors that can affect urine quality:
- Hydration: The amount of water a person drinks can have a significant impact on urine quality. Dehydration can result in concentrated urine that is darker in color and has a stronger odor. On the other hand, overhydration can lead to diluted urine that is lighter in color and may be more difficult to analyze.
- Diet: Certain foods and beverages can affect urine quality. For example, foods high in vitamin C can cause urine to be more acidic, while asparagus can cause a strong odor in urine. Beverages such as coffee and alcohol can also affect urine color and odor.
- Medications: Certain medications can impact the composition and quality of urine. For example, diuretics can increase urine output and cause dehydration, while antibiotics can change the color and odor of urine.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions can also affect urine quality. For example, kidney disease can lead to protein or blood in urine, while diabetes can cause sweet-smelling urine.
- Menstrual cycle: In women, the menstrual cycle can affect urine quality. During menstruation, blood may mix with urine and affect its color and odor.
It is important to be aware of these factors and how they can affect urine quality. If you are collecting urine for a medical test, it is recommended to follow any instructions provided by your healthcare provider and to inform them of any factors that may impact urine quality. This can help ensure accurate and reliable test results.
Best Practices For Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy testing is an important process for determining whether or not a person is pregnant. Here are some best practices for pregnancy testing to ensure accurate and reliable results:
- Follow the instructions provided: Different pregnancy tests may have different instructions for use, so it is important to carefully read and follow the instructions provided with the specific test you are using.
- Use first-morning urine: Using first-morning urine for a pregnancy test is generally recommended as it is more concentrated and may contain higher levels of the pregnancy hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin).
- Wait until the appropriate time to test: The accuracy of a pregnancy test can be impacted by when it is taken. It is recommended to wait until at least a week after a missed period before taking a pregnancy test. If you are unsure of when to test, consult with a healthcare provider.
- Store urine properly: If you need to store urine for a pregnancy test, make sure to store it in a clean, sterile container and keep it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. It is recommended to use stored urine within 24 hours.
- Confirm results with a healthcare provider: While home pregnancy tests are generally reliable, it is recommended to confirm results with a healthcare provider. A healthcare provider can conduct a blood test or ultrasound to confirm pregnancy and provide appropriate care.
- Seek medical attention if necessary: If a pregnancy test is positive, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible to begin appropriate prenatal care. If a pregnancy test is negative but pregnancy is still suspected, consult with a healthcare provider to determine the next steps.
Overall, following these best practices for pregnancy testing can help ensure accurate and reliable results. If you have any concerns or questions about pregnancy testing, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the accuracy of a pregnancy test is dependent on several factors, including the method of testing, the sensitivity of the test, and the freshness and quality of the urine used. While it is recommended to use urine that is collected on the day of the test or shortly before, some tests may allow for urine that has been stored for a few days, provided it has been stored properly in a clean, dry container in a cool place.
It is essential to follow the instructions on the pregnancy test carefully and to use urine that is within the recommended time frame to avoid inaccurate results. Waiting too long to test the urine can lead to a false negative result, even if the woman is actually pregnant. Additionally, if the urine is not stored properly or if it is contaminated, it can also lead to inaccurate results. Therefore, it is essential to store urine properly and to follow best practices for taking a pregnancy test to ensure the most accurate results.
If you suspect you may be pregnant, it is important to remember that a pregnancy test is just the first step in confirming your pregnancy. If you receive a positive result, it is recommended to make an appointment with a healthcare provider to confirm the pregnancy and begin prenatal care. If the result is negative, but you still suspect you may be pregnant, it is best to wait a few days and take another test or consult with a healthcare provider.

